Why identifiy conformationals epitopes?
Epitope mapping is performed to identify the epitope to which a monoclonal antibody binds.
Conformational epitopes consist of residues that are scattered in the primary sequence but brought together through folding of the protein of interest. The determination of conformational epitopes is a major issue in the antibody field, the standard techniques for determining linear epitopes being ineffective.
Agro-Bio has therefore developed a robust method for identifying an antibody’s conformational epitopes using in situ proteolysis involving formation of an immobilized antigen-antibody complex, followed by mass spectrometry analysis.

Our method combines:
- proteolytic digestion
- isolation of the epitope peptides by affinity chromatography
- final analysis of the epitope fragments by mass spectrometry.
Two approaches are possible:
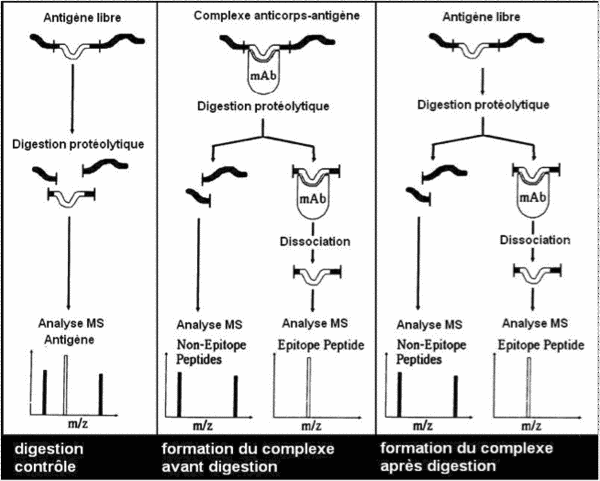
- the antigen/antibody complex is formed during affinity chromatography and the complex is digested within the affinity column
- antigen digestion is performed before formation of the antigen/antibody complex inside the affinity column.
Identification of the sequence of interest is based on the fact that antigen/antibody complex formation protects the epitope from enzyme digestion.
After affinity chromatography and digestion, the epitope fragments are eluted then sequenced by mass spectrometry: MALDI-TOF/TOF.
Epitope Mapping by Agro-Bio, the key advantages
Three expertises, Enzyme study, Purification, Mass spectrometry:
In a first phase, in silico study is employed to reduce the wet lab experiments, focusing on potential candidates containing selected protein features. At this point, a large number of peptides are screened via computer simulation and the most promising one is identified (at least 2 protease enzymes are selected).
In the second control phase, in-solution proteolytic digestion of Antigen and Antibody is performed in order to determine the digestion temperature and all peptides including the epitope sequences together with non- epitope peptides from the same protein or from other (if there is any contaminant). The success of the proteolysis reaction is then monitored by mass spectrometric peptide mapping.
In the final phase, an affinity chromatography column bounded with an immobilized antibody is used for the epitope extraction. The formation of Antibody-Antigen complex in the column is followed by an enzymatic digestion which is based on in silico study information. All unbounded peptides are washed off and the separated epitope peptides of interest by affinity chromatography are dissociated from the immobilized antibody by elution with low pH buffer and then sequenced by high resolution mass spectrometry.

